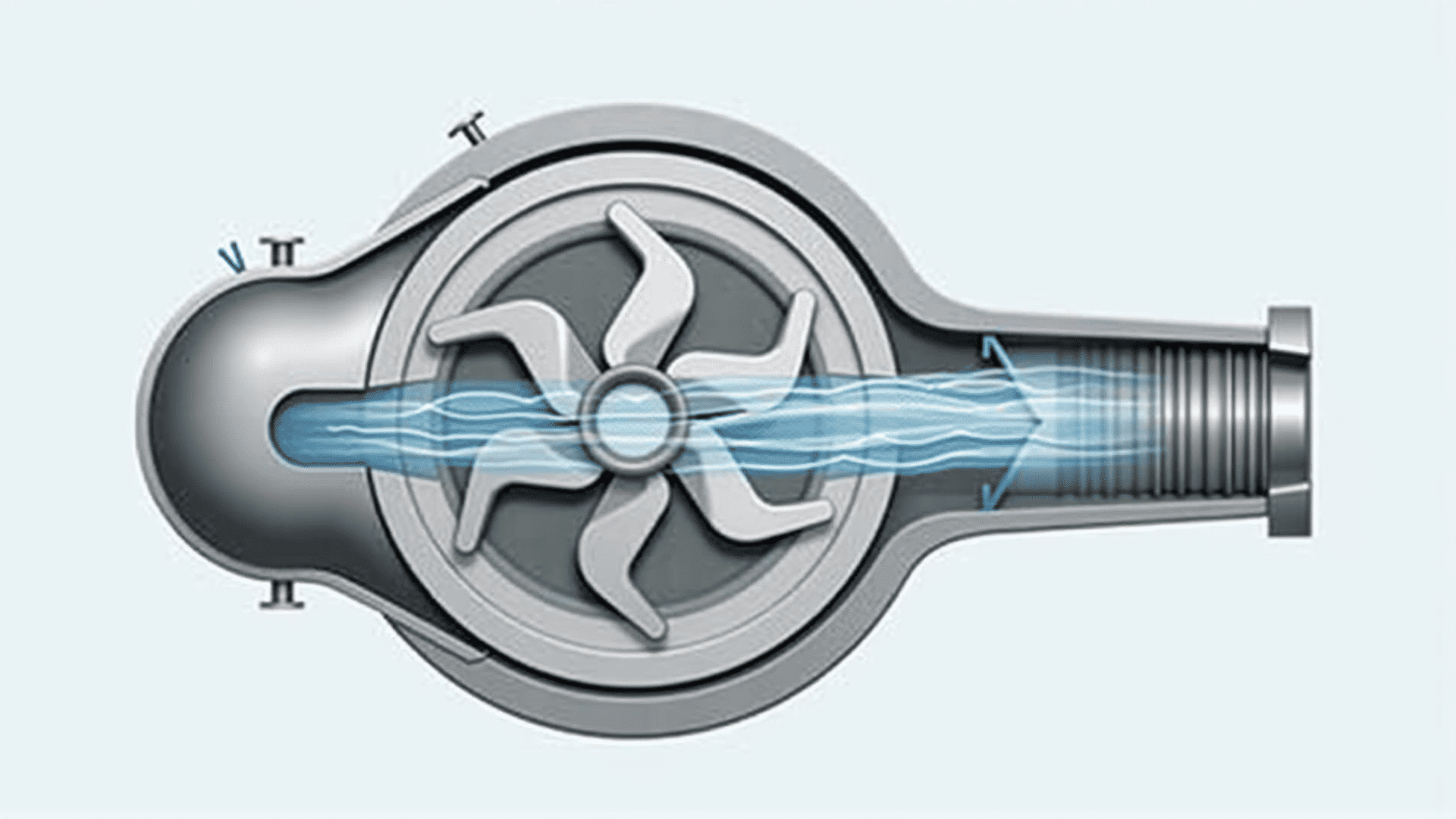
Centrifugal pumps are fundamental components in numerous industrial and household systems, playing a critical role in the movement of fluids. Understanding their principles is essential for anyone involved in fluid dynamics and related fields.
At their core, centrifugal pumps operate on the principle of centrifugal force. When the pump is activated, an impeller within the device spins, imparting energy to the fluid. This action converts mechanical energy from a motor into kinetic energy, which is then used to push the liquid outward from the pump’s center. As the fluid is expelled, it creates a vacuum that draws more fluid into the pump, allowing for continuous flow.
One of the key advantages of centrifugal pumps is their ability to handle large volumes of fluid. Unlike positive displacement pumps, which deliver a set amount of fluid per cycle, centrifugal pumps are designed to suit high flow rate applications. This makes them ideal for uses where the movement of significant fluid quantities is necessary, such as in water supply and treatment facilities, oil and gas operations, and chemical processing plants.
In terms of design, centrifugal pumps are relatively simple, often comprising an electric motor, a casing, and an impeller. The simplicity of these components contributes to the pump's durability and ease of maintenance. The casing of the pump is usually designed to guide the fluid flow and convert the discharge flow's kinetic energy into pressure energy.
Different types of centrifugal pumps are available, tailored for specific needs. For example, single-stage pumps feature one impeller and are suitable for low-pressure requirements. Multistage pumps, in contrast, have multiple impellers and can provide higher pressures. Depending on the application, material choices for the pump can range from stainless steel, which offers corrosion resistance, to plastic composites for less demanding environments.
The versatility of centrifugal pumps extends to their ability to handle various types of fluids, whether water, slurries, or viscous fluids. They can also be designed to manage varying temperature and pressure conditions, enhancing their adaptability across industries.
Maintaining centrifugal pumps involves regular inspection of the impeller and seals to ensure efficient operation. It is essential to avoid running the pump dry, as this can lead to overheating and damage. Proper lubrication of the bearings and monitoring for unusual noises or vibrations can also help extend the pump's lifespan.
In conclusion, centrifugal pumps are vital to the seamless operation of many systems, owing to their ability to efficiently move fluids across short and long distances. Their straightforward design and adaptability to different operational conditions make them a preferred choice across various industries. Understanding their mechanics and applications enables better system design and operation, ensuring efficient fluid management.